前言
Vue 是一个用于构建用户界面的渐进式框架,目前正在被越来越多的开发人员学习和使用。组件库可以帮助我们节省开发精力,无需一切从头开始,并且我们可以通过将小组件拼接在一起得到我们想要的最终页面。如果日常开发没有具体的业务需求,使用组件库进行开发无疑更加实用、高效,质量也相对更高。
本文一步步讲解了如何基于Vue构建UI组件库。
组件库官网
github地址
npm地址
1. 工艺表
首先我们简单了解一下构建UI组件库所涉及的技术栈。以下是我选择的:
- vue-cli:官方支持的 CLI 脚手架,提供现代的零配置构建设置;
- Vue:渐进式 JavaScript 库;
- Jest:用于单元测试组件库的 JavaScript 测试框架;
二.组件开发
项目初始化
开始,需要创建一个空的vue项目,在此基础上我们就可以开始编写接下来的组件库了!
npm i -g vue-cli // yarn add global vue-cli
vue init webpack heaven-ui //(heaven-ui)可以随意更换成你的名称
cd heaven-ui
npm run dev
我们安装好依赖并进入项目启动服务后,vue-cli3会自动给我们展示一个默认页面。这里我使用sass来美化ui组件的样式。
目录结构
|- build/ # webpack打包配置
|- lib/ # 打包生成的文件放这里
|- src/ # 在这里写代码
|- components/ # 各个组件,每个组件是一个子目录
|- mixins/ # 复用的mixin
|- utils # 工具目录
|- App.vue # 本地运行的开发预览
|- index.js # 打包入口,组件的导出
|- main.js # 本地运行的运行
|- static/ # 存放一些额外的资源文件,图片之类的
|- test/ # 测试文件夹
|- specs/ # 存放所有的测试用例
|- jest.conf.js/ # jest单元测试配置
|- .npmignore
|- .gitignore
|- .babelrc
|- README.md
|- package.json
组件库结构
显示所有组件的入口点,组件的详细代码仅显示按钮部分
src/components/index.js
import Alert from './components/alert/index.js'
import Button from './components/button/index.js'
import ButtonGroup from './components/button-group/index.js'
import Checkbox from './components/checkbox/index.js'
import CheckboxGroup from './components/checkbox-group/index.js'
import DatePicker from './components/date-picker/index.js'
import Form from './components/form/index.js'
import FormItem from './components/form-item/index.js'
import Icon from './components/icon/index.js'
import Input from './components/input/index.js'
import Option from './components/option/index.js'
import Pagination from './components/pagination/index.js'
import Radio from './components/radio/index.js'
import RadioGroup from './components/radio-group/index.js'
import Rate from './components/rate/index.js'
import Select from './components/select/index.js'
import Switch from './components/switch/index.js'
import Table from './components/table/index.js'
import HTableColumn from './components/table-column/index.js'
import Tag from './components/tag/index.js'
const components = [
Button,
ButtonGroup,
Checkbox,
CheckboxGroup,
DatePicker,
Form,
FormItem,
Icon,
Input,
Option,
Pagination,
Radio,
RadioGroup,
Rate,
Select,
Switch,
Table,
HTableColumn,
Tag,
]
const install = function(Vue, opts = {}) {
components.map(component => {
Vue.component(component.name, component);
})
Vue.prototype.$alert = Alert;
}
/* 支持使用标签的方式引入 */
if (typeof window !== 'undefined' && window.Vue) {
install(window.Vue);
}
export default {
install,
Alert,
Button,
ButtonGroup,
Checkbox,
CheckboxGroup,
DatePicker,
Form,
FormItem,
Icon,
Input,
Option,
Pagination,
Radio,
RadioGroup,
Rate,
Select,
Switch,
Table,
HTableColumn,
Tag,
}
src/components/button/index.js
import HButton from './src/button';
HButton.install = function(Vue) {
Vue.component(HButton.name, HButton);
};
export default HButton;
组成部分是这样的
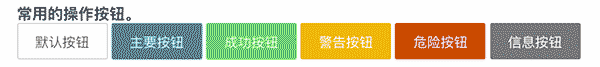

封装配置
目录创建完成后,就该填血了。要打包一个组件库项目,我们首先要配置我们的webpack,否则写完源码后我们无法运行它。所以我们先找到建筑目录
webpack.base.js。保存一些基本规则配置
webpack.prod.js。整个元件库的封装配置
build/webpack.base.conf.js
'use strict'
const path = require('path')
const utils = require('./utils')
const config = require('../config')
const vueLoaderConfig = require('./vue-loader.conf')
function resolve (dir) {
return path.join(__dirname, '..', dir)
}
module.exports = {
context: path.resolve(__dirname, '../'),
entry: {
app: process.env.NODE_ENV === 'production' ? './src/index.js' : './src/main.js'
},
output: {
path: config.build.assetsRoot,
filename: '[name].js',
publicPath: process.env.NODE_ENV === 'production'
? config.build.assetsPublicPath
: config.dev.assetsPublicPath
},
resolve: {
extensions: ['.js', '.vue', '.json'],
alias: {
'vue$': 'vue/dist/vue.esm.js',
'@': resolve('src'),
'untils': resolve('src/untils'),
}
},
module: {
rules: [
{
test: /\.vue$/,
loader: 'vue-loader',
options: vueLoaderConfig
},
{
test: /\.js$/,
loader: 'babel-loader',
include: [resolve('src'), resolve('test'), resolve('node_modules/webpack-dev-server/client')]
},
{
test: /\.(png|jpe?g|gif|svg)(\?.*)?$/,
loader: 'url-loader',
options: {
limit: 10000,
name: utils.assetsPath('img/[name].[hash:7].[ext]')
}
},
{
test: /\.(mp4|webm|ogg|mp3|wav|flac|aac)(\?.*)?$/,
loader: 'url-loader',
options: {
limit: 10000,
name: utils.assetsPath('media/[name].[hash:7].[ext]')
}
},
{
test: /\.(woff2?|eot|ttf|otf)(\?.*)?$/,
loader: 'url-loader',
options: {
limit: 10000,
name: utils.assetsPath('fonts/[name].[hash:7].[ext]')
}
},
{
test: /\.scss$/,
loaders:['style','css','sass']
}
]
},
node: {
// prevent webpack from injecting useless setImmediate polyfill because Vue
// source contains it (although only uses it if it's native).
setImmediate: false,
// prevent webpack from injecting mocks to Node native modules
// that does not make sense for the client
dgram: 'empty',
fs: 'empty',
net: 'empty',
tls: 'empty',
child_process: 'empty'
}
}
build/webpack.prod.conf.js
'use strict'
const path = require('path')
const utils = require('./utils')
const webpack = require('webpack')
const config = require('../config')
const merge = require('webpack-merge')
const baseWebpackConfig = require('./webpack.base.conf')
const ExtractTextPlugin = require('extract-text-webpack-plugin')
const OptimizeCSSPlugin = require('optimize-css-assets-webpack-plugin')
const UglifyJsPlugin = require('uglifyjs-webpack-plugin')
const env = require('../config/prod.env')
const webpackConfig = merge(baseWebpackConfig, {
module: {
rules: utils.styleLoaders({
sourceMap: config.build.productionSourceMap,
extract: true,
usePostCSS: true
})
},
devtool: config.build.productionSourceMap ? config.build.devtool : false,
output: {
path: config.build.assetsRoot,
filename: 'heaven-ui.min.js',
library: 'heaven-ui',
libraryTarget: 'umd'
},
plugins: [
// http://vuejs.github.io/vue-loader/en/workflow/production.html
new webpack.DefinePlugin({
'process.env': env
}),
new UglifyJsPlugin({
uglifyOptions: {
compress: {
warnings: false
}
},
sourceMap: config.build.productionSourceMap,
parallel: true
}),
// extract css into its own file
new ExtractTextPlugin({
filename: 'heaven-ui.min.css',
}),
// Compress extracted CSS. We are using this plugin so that possible
// duplicated CSS from different components can be deduped.
new OptimizeCSSPlugin()
]
})
if (config.build.productionGzip) {
const CompressionWebpackPlugin = require('compression-webpack-plugin')
webpackConfig.plugins.push(
new CompressionWebpackPlugin({
asset: '[path].gz[query]',
algorithm: 'gzip',
test: new RegExp(
'\.(' +
config.build.productionGzipExtensions.join('|') +
')$'
),
threshold: 10240,
minRatio: 0.8
})
)
}
if (config.build.bundleAnalyzerReport) {
const BundleAnalyzerPlugin = require('webpack-bundle-analyzer').BundleAnalyzerPlugin
webpackConfig.plugins.push(new BundleAnalyzerPlugin())
}
module.exports = webpackConfig
这里我配置了输出目录为lib,打包结果如下:
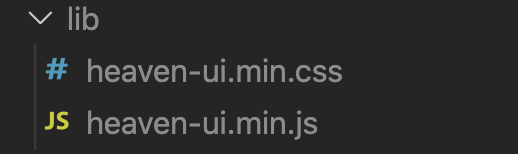

3。单元测试
单元测试具有以下优势:
1。可以检测功能的隐藏错误
2。确保代码重构的安全。
组件库中的每个组件都可以重构或更新迭代。如果单元测试覆盖率高,则代码更改后更容易发现潜在的问题。例如,版本升级后,某些功能缺失。
组件库开发调试完成后,我们需要编写每个组件对应的单元测试,以达到100%覆盖率的目标。
以按钮为例:测试/规格/Button.spec.js
import Vue from 'vue'
import Button from '@/components/button'
describe('button.vue', () => {
it('button是否存在',()=>{
expect(Button).to.be.ok;
})
})
4。发布 NPM
在发布npm之前,我们需要根据npm的合约规则编写package.json。我们来解决组件库打包问题。首先,我们需要让脚手架编译我们的组件代码并发送到指定目录,我们通常按照合约交付规范输出到lib目录。项目打包后,我们需要将描述、关键字等写入打包文件中。详情如下:
description 元件库的描述文字
关键字 组件库关键字
许可证
repository 组件库关联的Git仓库地址
homepage 元件库显示的第一页地址
main 组件库主入口地址(使用组件时引入的地址)
private声明组件库的隐私性。如果要发布到公共npm网络上,请删除该属性或将其设置为false
publishConfig 用于设置npm发布的地址。这个配置对于团队中的npm服务器非常关键,可以设置为私有npm仓库
发布到npm的方法也很简单。首先我们需要在npm官网注册一个账号,然后登录控制台。最后我们执行npmpublish,即
是的。具体流程如下:
// 登录
npm login
// 发布
npm publish
// 如果发布失败提示权限问题,请执行以下命令
npm publish --access public
注:本出版物版本号需要修改
5。总结
我们可以使用vue-cli或者其他工具生成另一个demo项目,并使用这个项目来引入我们的组件库。如果您的包尚未发布,您可以在
找到它在组件库的项目目录下,使用npm link或yarn link命令创建链接
然后在demo目录中使用npm link packagename或yarnlink packagename,其中packagename是组件库的
包名,然后在demo工程的入口文件中
import Vue from vue
import Heaven from 'heaven-ui'
import 'heaven-ui/dist/heaven-ui.min.css'
// 其他代码 ...
Vue.use(Heaven)
这样设置后,我们创建的组件就可以在这个项目中使用了
 code前端网
code前端网


